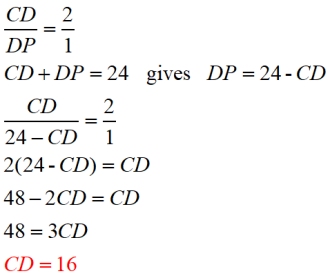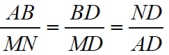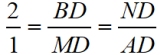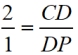|
Things to remember before we begin:
• The "centroid" of a triangle is the point of concurrency
for the three medians of the triangle.
• The median of a triangle connects a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
• A point of concurrency is the point where all three medians intersect. |
The "Centroid" Theorem says that the location of the point, called the centroid, divides each of the medians of the triangle into a ratio of 2:1. The longer portion of the median will be connected to the vertex of the triangle.

Given diagram shown.
If
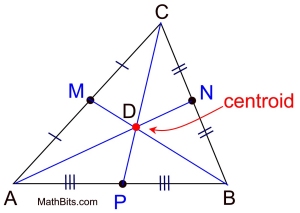
CP = 24", find CD.
After finding the answer, we can
see that CD : DP = 16 : 8 = 2 : 1.
|
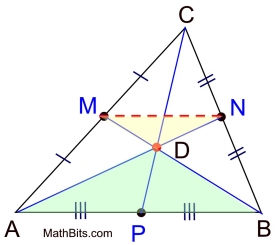
The diagram shows ΔABC with all 3 medians drawn and centroid (point D) labeled.
CP = 24"
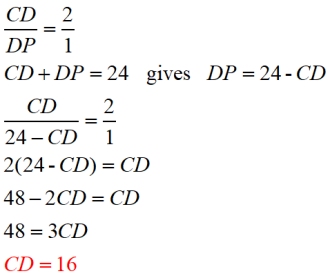
|
|
(Centroid Theorem): The centroid of a triangle divides each median in the ratio 2 : 1. (proof below) |
|
The proof of this theorem will concentrate on establishing ratios
(AD : DN and BD : DM) to be equivalent to 2 : 1.
The other median ratio can follow this same procedure.
Proof:
Statements |
Reasons |
1. D centroid, midpts M,N,P |
1. Given |
2. 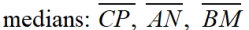 |
2. Median of a Δ connects the vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. |
3. Connect midpoint M to midpoint N |
3. Two points determine one, and only one straight line. |
4. 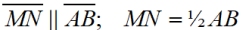 |
4. The mid-segment of a Δ (connecting the midpts of two sides) is || to the 3rd side and ½ the 3rd side. |
5. ∠ NMB 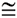 ∠ MBA
∠ MNA 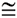 ∠ NAB |
5. If 2 || lines are cut by a transversal, the alternate interior angles are congruent. |
6. Δ MND  Δ BAD |
6. AA: If 2 ∠s of one Δ are 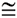 to the corresponding ∠s of another Δ, the Δs are similar. |
7. 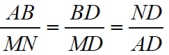 |
7. Corresponding side of similar triangle are in proportion. |
8. 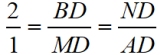 |
8. Substitution (from step 4) |
9. 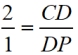 |
9. Repeat this process connecting point M to point P. |

NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in part or whole) from this site to the Internet
is copyright violation
and is not considered "fair use" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use". |
|