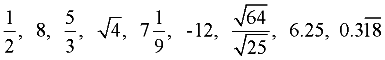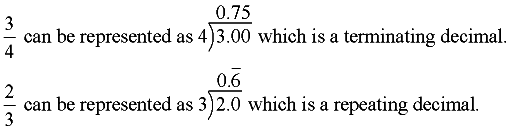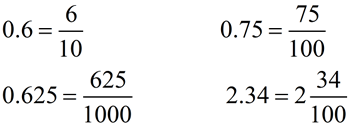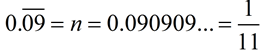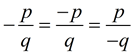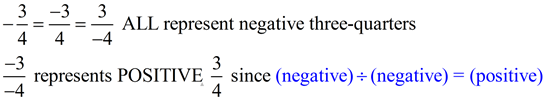|
Rational numbers are numbers that look like fractions (ratios), or can be written as a fraction, with the numerator and denominator being integers (denominator not equal to zero).
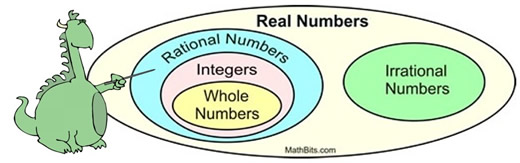
In the diagram at the right, you can see that the Real Numbers have two large subsets called "Rational Numbers" and "Irrational Numbers".
|
|
Since rational numbers are a subset of the real numbers,
they possess all of the properties assigned to the real number system.
 |
A rational number is a number that can be expressed as a fraction (ratio) in the form 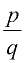 where p and q are integers and q is not zero. where p and q are integers and q is not zero. |
|
Examples: 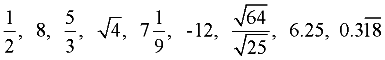
 When a rational number fraction is divided to form a decimal value, When a rational number fraction is divided to form a decimal value,
it becomes a terminating decimal, such as 6.25, or a repeating decimal, such as  . .
Every number has a decimal expansion.
 To convert a fraction to a decimal: To convert a fraction to a decimal: |
A fraction is converted to a decimal by dividing the bottom (denominator)
into the top (numerator).
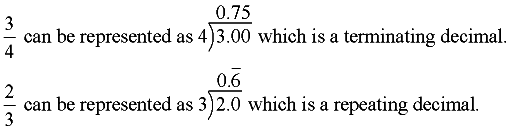
[Notice that a repeating decimal has a "bar" over the top of the repeating pattern.]
These are rational values.
Your calculator may not see all repeating decimal patterns!
Some rational fractions may produce a large number of digits in their repeating patterns, which may exceed the size of the viewing screen on a calculator. The fraction 53/83 has a calculator display of 0.6385542169, which shows no repeating pattern, when in reality the pattern will repeat after 41 digits. |
 To convert a decimal to a fraction: To convert a decimal to a fraction: |
A decimal is converted to a fraction by placing the decimal number
over its place value.
 Place Values
Place Values |
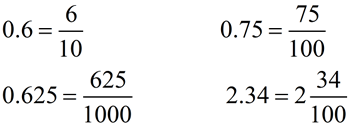 These fractions can be simplified.
These fractions can be simplified. |
 To convert a repeating decimal to a fraction: To convert a repeating decimal to a fraction:
This topic was omitted for Next Generation Standards. |
Write 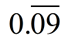 as a fraction. as a fraction.
This is going to take more work than just looking at the place value, as was done above. The definition of a rational number is that it can be written in fraction form with the numerator (and denominator) being integers. Since a repeating decimal is not an integer, we cannot use it as a numerator and place it over one, such as 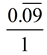 . .
We need another strategy to eliminate the repeating decimal. We are going to express our repeating decimal as a variable and then work on getting rid of the decimal.

We now know that our repeating decimal, is equal to the fraction 1/11.
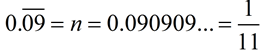
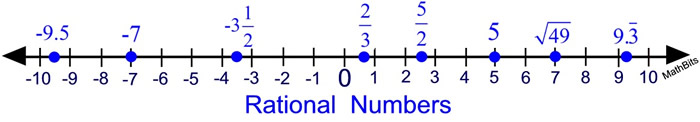
 Rationals on a Number Line: Rationals on a Number Line: |
A number line is a straight line diagram on which every point corresponds to a real number.
Since rational numbers are real numbers, they have a specific location on a number line.
Rational numbers can be ordered on a number line.
 Signs and Rational Values (Fractions): Signs and Rational Values (Fractions): |
If p and q are integers (with q not zero), then 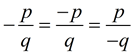 . . 
Notice that the negative sign can be "out front", "top only", or "bottom only" and all three fractions represent the same value.
 Putting a negative sign BOTH "top" and "bottom" will yield a different result. Putting a negative sign BOTH "top" and "bottom" will yield a different result.
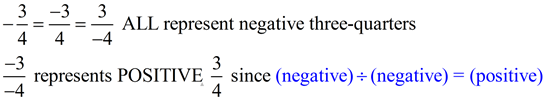
|