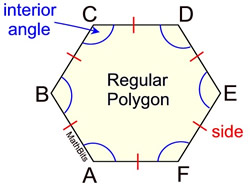
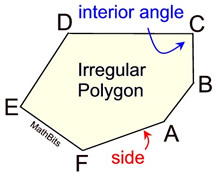
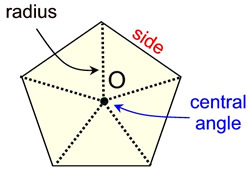
You have already been working with some regular polygons.
The table below shows some of the more commonly used polygons. Do NOT assume that the diagrams in the "Figure" column are "regular" polygons.
Topical Outline | JrMath Outline | MathBitsNotebook.com | MathBits' Teacher Resources
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||