|
1. Start with a quadratic equation set = 0.
|
|
2. Move the constant to the right side. |
|
3. Divide each term by a to get the leading coefficient to be one. |
|
4. Get ready for a perfect square trinomial on the left side (put in the boxes). |
|
5. To find the needed value, take half of the coefficient of the x-term, 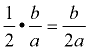 , and square it, 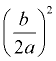 . Add this value to both sides of the equation (put it in the boxes). |
|
6. Square the last term on the right side. Find a common denominator on the right. |
|
7. Combine terms on the right, placing b2 in front of -4ac in the numerator. |
|
8. Re-write the perfect square trinomial on the left side as the square of a binomial. |
|
9. Take the square root of both sides. Simplify the radical on the right side. |
|
10. Subtract the constant away from x. Write as a single fraction on the right side. |