|

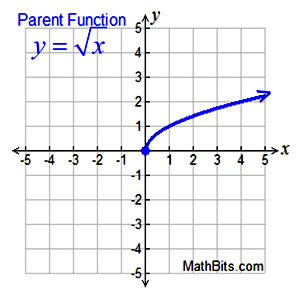
Unless otherwise stated:
Domain: x > 0 or [0,∞)
Range: y > 0 or [0,∞)
|
Features (of parent function):
• increasing function [0,∞)
• positive function (0,∞)
• no absolute max (graph → ∞)
• absolute minimum 0
• no relative max/min
• end behavior
as x → +∞, f (x)
→ +∞
as x → 0+, f (x)
→ 0
|
|
Average rate of change: (slope) NOT constant.
x-intercept:
intersects x-axis at
(0, 0)
unless domain is altered
y-intercept:
intersects y-axis at
(0, 0)
unless domain is altered
Note:
This function is the positive square root only.
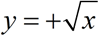 |
|
Table:
Y1: 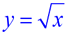
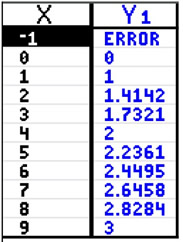 Remember: The square root of a negative number is imaginary. Remember: The square root of a negative number is imaginary. |
Connection to y = x²:
[Reflect y = x² over the line y = x.]
If we solve y = x² for x: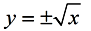 , we get the inverse.
We can see that the square root function is "part" of the inverse of y = x². , we get the inverse.
We can see that the square root function is "part" of the inverse of y = x².
Keep in mind that the square root function only utilizes the positive square root. If both positive and negative square root values were used, it would not be a function. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
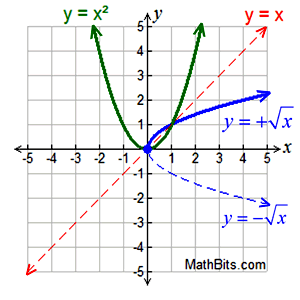
Square Root Function - Transformation Examples:
 Translations
Translations |
Translations:
Vertical Shift: f (x) + k
Horizontal Shift: f (x + k)
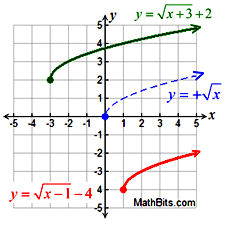
Reflections:
-f (x) over x-axis
f (-x) over y-axis
|
Reflection |
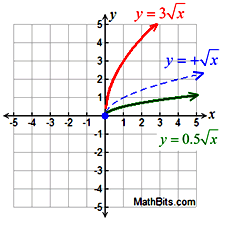 Vertical Stretch/Compress Vertical Stretch/Compress |
Vertical Stretch/Compress
k • f (x) stretch (k > 1)
k • f (x) compress (0 < k < 1)
Horizontal Stretch/Compress
f (k • x) stretch (0 < k < 1)
f (k • x) compress ( k > 1) |
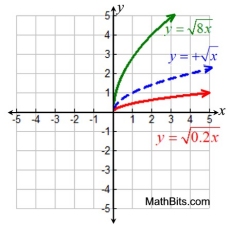 Horizontal Stretch/Compress Horizontal Stretch/Compress |
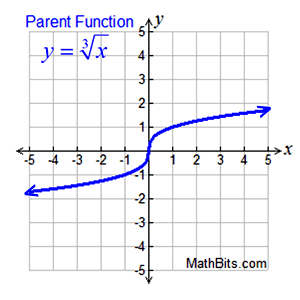 Unless otherwise stated:
Domain: All Reals or (-∞,∞)
Range: All Reals or (-∞,∞)
|
Features (of parent function):
• increasing (-∞,∞)
• positive (0,∞)
• negative (-∞,0)
• no absolute max (graph → ∞)
• no absolute min (graph→ -∞)
• no relative max or min
• end behavior
as x → +∞, f (x)
→ +∞
as x → -∞, f (x)
→ -∞
|
|
Average rate of change: (slope) NOT constant.
x-intercept:
intersects x-axis at
(0, 0)
unless domain is altered
y-intercept:
intersects y-axis at
(0, 0)
unless domain is altered
Note:
Unlike the square root function, the cube root function can process negative values.
|
Table:
Y1: 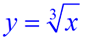
Remember: The cube root function
can process negative x-values. |
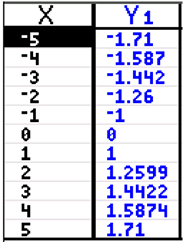
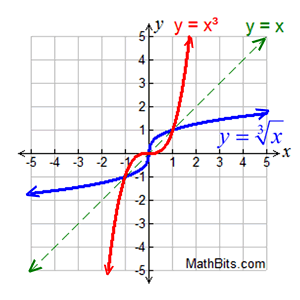
Connection to y = x³:
[Reflect y = x³ over the line y = x.]
If we solve y = x³ for x:
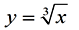 , we get the inverse. , we get the inverse.
We can see that the cube root function is the inverse of y = x³.
Remember that the cube root function can process negative values, such as: 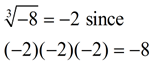 |
 |
|
|
Cube Root Function - Transformation Examples:
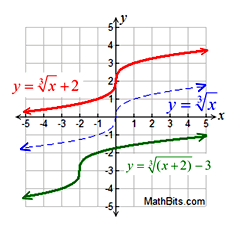 Translations
Translations |
Translations:
Vertical Shift: f (x) + k
Horizontal Shift: f (x + k)
Reflections:
-f (x) over x-axis
f (-x) over y-axis
|
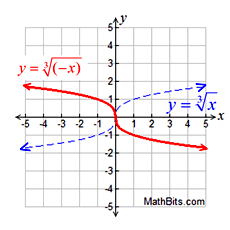
Reflection |
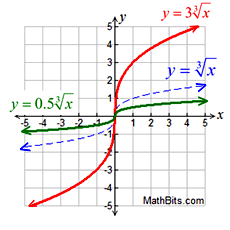 Vertical Stretch/Compress
Vertical Stretch/Compress |
Vertical Stretch/Compress
k • f (x) stretch (k > 1)
k • f (x) compress (0 < k < 1)
Horizontal Stretch/Compress
f (k • x) stretch (0 < k < 1)
f (k • x) compress ( k > 1) |
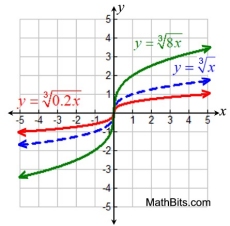
Horizontal Stretch/Compress |

NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in part or whole) from this site to the Internet
is copyright violation
and is not considered "fair use" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use". |
|

