|
A radical expression is one which contains a root (square root, cube root, etc.).
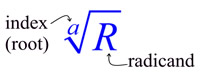 
In Algebra 1, radical expressions are primarily limited to square root (a = 2) expressions and cube root (a = 3) expressions.
On this page, the radicand will be non-negative. No negatives under the radical.]
Square roots have an index value of two. When you see a radical with no index listed, it is assumed to be an index of two, a square root.
To take the square root of a number,
is to un-do (or reverse) the squaring process.
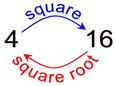
Finding the square root of a number is the inverse operation of squaring the number.
4 squared = 16
square root of 16 = 4 |
 |
Squaring: 92 = 81 Square rooting: 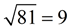
 
It is important to remember that if there is NO SIGN in front of a square root symbol, you are dealing with the positive answer only. The positive sign is implied to be there, indicating the principal square root.
If a negative symbol is in front of a square root symbol, the answer will be negative.

The square root of a value is a quantity which, when squared, equals the radicand (the number under the square root symbol.) For example, the square root of 16 could be either + 4 or -4, since both, when squared, equal 16.
It is understood, however, that the square root (radical) symbol denotes only the positive root, called the "principal square root". 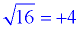 When solving the equation x2 = 25, you are searching for both solutions: +5 and -5. So, we write: 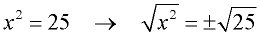
|
"Cubing" is the same as raising to the power of 3,
denoted by an exponent of 3.
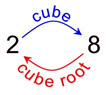
To take the cube root of a number,
is to un-do (or reverse) the cubing process.
Finding the cube root of a number is the inverse operation of cubing the number.
2 cubed = 8
cube root of 8 = 2 |
 |
Cubing: 43 = 64 Cube rooting: 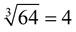
|
The radical symbol used for a cube root requires
an index (root) of 3, which must always appear in the symbol.
When working with cube roots, the sign inside the cube root symbol
will determine the sign of the answer.
You may see a negative number under a cube root symbol.
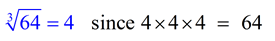
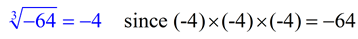 |
Perfect Squares
0 = 0 x 0
1 = 1 x 1
4 = 2 x 2
9 = 3 x 3
16 = 4 x 4
25 = 5 x 5
36 = 6 x 6
49 = 7 x 7
64 = 8 x 8
81 = 9 x 9
100 = 10 x 10
121 = 11 x 11
144 = 12 x 12
169 = 13 x 13
196 = 14 x 14
225 = 15 x 15 |
Perfect Cubes
0 = 0 x 0 x 0
1 = 1 x 1 x 1
8 = 2 x 2 x 2
27 = 3 x 3 x 3
64 = 4 x 4 x 4
125 = 5 x 5 x 5
216 = 6 x 6 x 6
243 = 7 x 7 x 7
512 = 8 x 8 x 8
729 = 9 x 9 x 9
|
\
|