|
A mathematical "expression" may be either a numerical expression, such as 12 + 32, or an algebraic expression, such as 12 + n. The result of all "numerical" expressions is constant (it does not change). While the result of an "algebraic" expression can be constant (such as 5x0), the result of an algebraic expression most generally changes, based on the value that replaces the variable.

Unlike equations, algebraic expressions do not contain an equal sign.
|
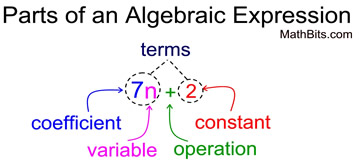
• The word "terms" (or algebraic terms) are the parts of an expression that are being added and/or subtracted.
7n + 2 has two terms.
• The word "factors" refers to values that are multiplied. The term 7n has two factors: 7 and n.
|
• The word "variable" refers to a letter representing a value that can change.
• The word "coefficient" refers to a number that is multiplied times a variable. It is the number "out front" of the variable.
• The word "constant" refers to a number by itself (a value that will not change).
• The word "operation" refers to a mathematical operation such as adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing.
•
The word "exponent" refers to any power that may be associated with a variable.
 Note: keep in mind that n and n2 involve the same Note: keep in mind that n and n2 involve the same
variable n, but are not "like" terms, and cannot be added.
|
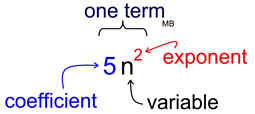 |
• The word "degree" of an algebraic expression (in one variable) is the highest exponent of the variable in that expression. If the expression is 5n2 (shown above), the degree is 2.
Classifications of Algebraic Expressions:
Algebraic Expressions Classified by Terms |
Monomial Expression |
one term: 12, 4x, x2, -5xy |
Binomial Expression |
two terms: 2x - 1, x2 - 4 |
Trinomial Expression |
three terms: x2 + 2x + 1 |
polynomial - one or more terms
polynomial means "many",
but it can also be one term. |
The ending of these words "nomial" is Greek for "part". |
Algebraic Expressions Classified by Degree |
Note: The largest exponent associated with an expression (in one variable)
is referred to as the "degree" of the expression. |
Linear Expression |
Linear - degree of 1 or 0: 3x + 1 or 12 |
Quadratic Expression |
Quadratic - degree of 2: 2x2 - x + 7 |
Cubic Expression |
Cubic - degree of 3: 3x3 + 4x2 + 3x + 5 |
The degree of a polynomial is the highest degree of its terms.
Example: 3x2 + 4x + 1 has a degree of 2
x3 - x2 + 5x - 2 has a degree of 3 |
Degree of a "Term" |
The degree of a "term" with whole number exponents is the sum of the exponents of the variables, if there are variables. Non-zero constants have degree 0, and the term zero has no degree.
Examples: 6x2 has a degree of 2
4x2y3 has a degree of 5 (the sum of 2 and 3)
The degree of the number 8 (a constant) is zero. |

NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in part or whole) from this site to the Internet
is copyright violation
and is not considered "fair use" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use". |
|