Practice Test 1 - Question 31
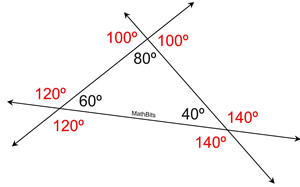
An exterior angle is formed by one side of the triangle and the extension of another side of the triangle, creating a linear pair at each vertex. Angles forming linear pairs are supplementary.
By convention, the "sum" of the exterior angles only counts ONE exterior angle at each vertex.
The sum of the three sets of linear pairs (one at each vertex) equals 540º. Subtracting the 180º for the sum of the angles in the triangle, we are left with 360º for the sum of the exterior angles.
All Rights Reserved - Copyright MathBitsNotebook.com