|
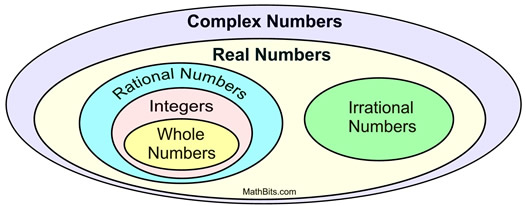
Most of the numbers we know, and work with, are Real Numbers. The Real Number System (symbol 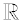 ) includes counting numbers, fractions, terminating decimals, positive numbers, negative numbers, zero, repeating decimals, never ending and non-repeating decimals, numbers that are expressed as radicals, and even pi ( π).
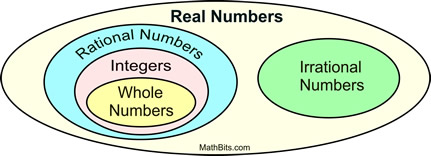
The set of Real Numbers contains a series of subsets of other number systems. |
|
|
The natural numbers appear within the set of whole numbers. |
• The natural numbers (symbol 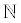 ) are the set of counting numbers {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ...}
• There are infinitely many numbers in this set of numbers.
|
• The whole numbers (symbol  ) )are the set of counting numbers (natural numbers) along with zero
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ...}
• There are infinitely many numbers in this set of numbers.
• The integers (symbol 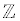 ) are the set of all of the natural numbers,
plus their additive inverses (their negatives), and zero {...-4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ....}
• The rational numbers (symbol 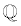 ) are the set of numbers which can be expressed as a ratio
(a fraction) between two integers.
• Integers are rational numbers since 5 can be written as the fraction 5/1.
• Decimals which terminate are rational numbers. 8.5 = 85/10
• Decimals which have a repeating pattern are rational numbers. 1/3 = 0.3333333...
• The irrational numbers are the set of number which can NOT be written as a ratio
(fraction).
• The symbol for Irrational numbers can be
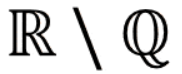 (meaning Reals minus Rationals), or (meaning Reals minus Rationals), or 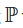 ) )
• Decimals which never end nor repeat are irrational numbers.
• Examples of irrational numbers: 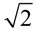 , π , π
Are there numbers that are not Real Numbers?
Actually, there is a another set of numbers, called Complex Numbers,
which contains the set of Real Numbers and some other interesting numbers.
The numbers that are in the set of Complex Numbers, but are NOT in the set of Real Numbers:
• the imaginary number, i, which is the square root of negative one.
• pure imaginary numbers of the form bi.
• complex numbers of the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers.
Imaginary numbers are essential to the study of sciences such as electricity, quantum mechanics, vibration analysis and cartography.)
Do not confuse "imaginary" numbers with "irrational" numbers.
Not the same creatures!

NOTE: The re-posting of materials (in part or whole) from this site to the Internet
is copyright violation
and is not considered "fair use" for educators. Please read the "Terms of Use". |
|